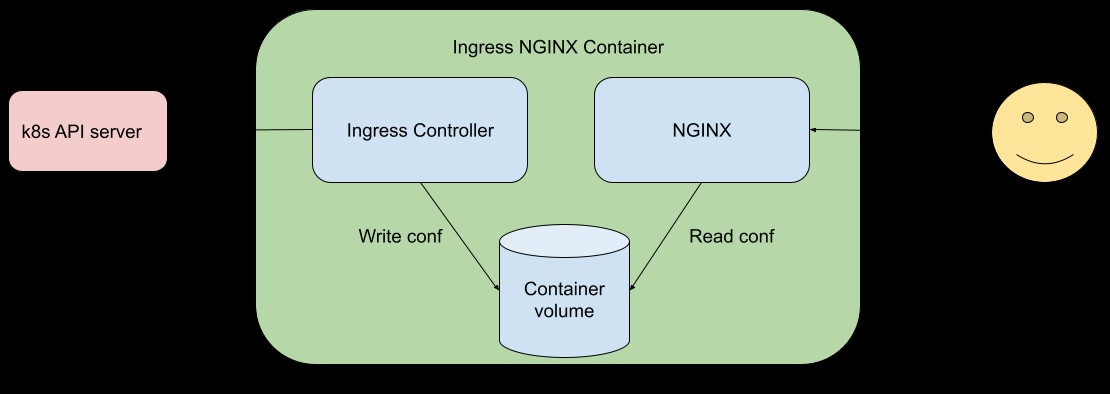
A set of dangerous security flaws have been discovered in the Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes, putting over 6,500 clusters at risk of remote code execution attacks. The vulnerabilities affect clusters exposed to the public internet and could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access without authentication.
The five vulnerabilities, collectively named "IngressNightmare," received a critical CVSS score of 9.8. Cloud security researchers at Wiz identified the flaws, which specifically impact the admission controller component of Ingress NGINX Controller.
Key Details
- Over 43% of cloud environments are vulnerable
- Affects admission controller component
- Allows unauthorized access to cluster secrets
- Can lead to complete cluster takeover
- Does not impact standard NGINX Ingress Controller
How the Attack Works
The vulnerabilities take advantage of the admission controller's network accessibility without authentication requirements. Attackers can inject malicious NGINX configurations by sending specially crafted ingress objects directly to the admission controller. This allows code execution within the controller's pod.
The identified vulnerabilities are:
- CVE-2025-24514: auth-url Annotation Injection
- CVE-2025-1097: auth-tls-match-cn Annotation Injection
- CVE-2025-1098: mirror UID Injection
- CVE-2025-1974: NGINX Configuration Code Execution
Recommended Actions
Organizations using Ingress NGINX Controller should:
Update to patched versions:
- Version 1.12.1
- Version 1.11.5
- Version 1.10.7
Implement security measures:
- Ensure admission webhook endpoint is not exposed externally
- Limit access to only the Kubernetes API Server
- Temporarily disable admission controller if immediate patching isn't possible
The research team worked closely with Kubernetes maintainers to address these vulnerabilities before public disclosure. Organizations are strongly advised to apply the security updates as soon as possible to protect their clusters from potential attacks.