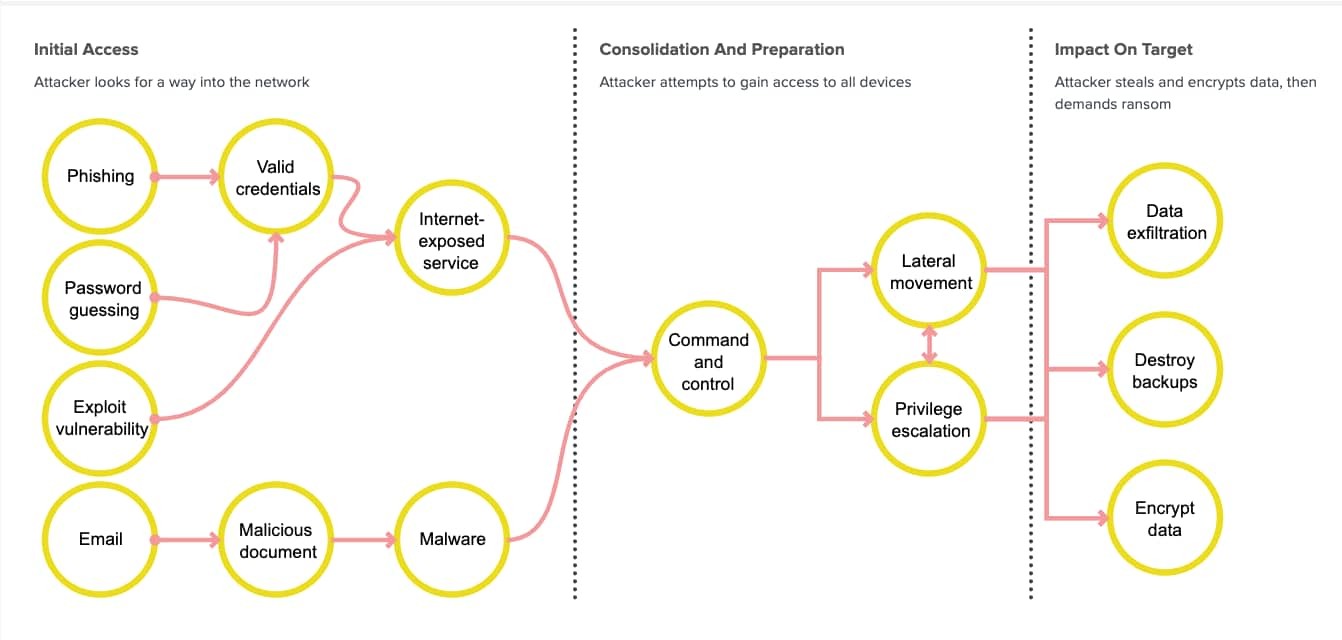
The landscape of ransomware attacks is evolving dramatically. While traditional ransomware encrypted files directly on victims' computers, modern attackers have shifted their focus to browser-based techniques that target cloud and SaaS applications where organizations now store their most valuable data.
The New Face of Account Compromise
Attackers employ multiple sophisticated methods to gain unauthorized access to accounts. They exploit authentication vulnerabilities, conduct large-scale password attacks, and manipulate OAuth and SAML workflows. For example, researchers recently discovered vulnerabilities in popular apps like Grammarly that allowed account takeovers through manipulated access tokens.
OAuth Permissions and Browser Extensions: Hidden Dangers
When users grant permissions to third-party applications through OAuth consent screens, they may unknowingly give attackers persistent access to their accounts. Malicious applications often request excessive permissions, allowing them to access and extract sensitive data without raising alerts.
Browser extensions pose another major risk. Operating with the same privileges as the browser itself, compromised extensions can silently harvest authentication tokens and manipulate web content without users noticing.
Advanced Social Engineering Tactics
Modern attackers employ sophisticated social engineering through:
- Brand impersonation using typosquatted domains
- Browser-in-the-middle attacks that intercept entire login processes
- Compromised password manager extensions
Why Traditional Security Falls Short
Once attackers gain access, they can delete data and demand ransoms while appearing as legitimate users. Most concerning is that these browser-native attacks operate completely outside traditional security tools' detection capabilities.
Since no malware is downloaded to computers, standard endpoint protection solutions cannot detect these attacks. The attacks leverage legitimate web protocols and APIs, making them virtually invisible to conventional security monitoring.
The Path Forward
Organizations must adapt their security approach to address these browser-based threats. Modern protection requires tools specifically designed to monitor browser activity, detect suspicious OAuth requests, and guard against malicious extensions.
With hundreds of potential browser-based entry points available to attackers, organizations need dedicated browser security solutions to effectively combat this emerging breed of ransomware attacks.