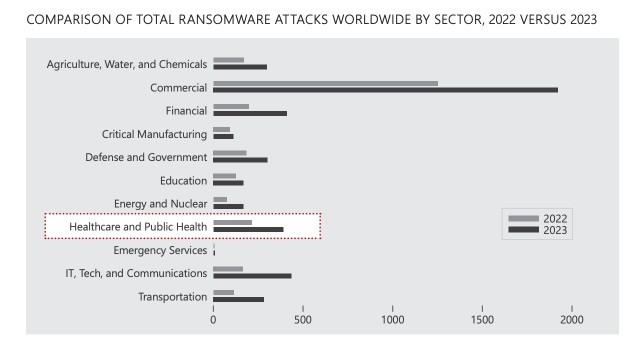
The healthcare sector faces an unprecedented surge in cybersecurity threats, with ransomware attacks doubling between 2022 and 2023, according to the Office of the Director of National Intelligence. Nearly 25% of these attacks utilized LockBit, a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) tool that operates like a commercial enterprise.
The rising wave of attacks poses severe risks beyond financial damage. During the COVID-19 pandemic peak in 2020, targeted hospital systems were forced to redirect patients and lost thousands of medical records, directly impacting patient care and safety.
Healthcare organizations face unique cybersecurity challenges due to their complex technology infrastructure and vast stores of protected health information (PHI). This sensitive data proves incredibly valuable to cybercriminals who can exploit it for identity theft, fraud, or black market sales. U.S. healthcare providers must also maintain compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations or face substantial penalties.
Research from the National Institute of Health (NIH) reveals that implementing robust data backup systems stands as one of the most effective defenses. Their analysis of hospital cyberattacks from 2016-2021 showed that approximately 20% of impacted healthcare organizations successfully recovered their data through backup systems.
The 3-2-1 backup strategy has emerged as a leading approach for healthcare cybersecurity. This method requires maintaining three total data copies across two different media types, with one copy stored off-site or in the cloud. This strategy provides quick data recovery options while protecting against network-wide compromises.
Alabama Cancer Care (ALCC) demonstrates how healthcare providers can implement comprehensive backup solutions across complex systems. With 15 locations and nearly two decades of patient records, ALCC needed to protect data across 250 Microsoft 365 accounts, multiple PCs, virtual machines, and servers - all while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
ALCC adopted a centralized backup system that unified management of their diverse data sources while enabling cloud storage for off-site protection. This approach follows the 3-2-1 backup rule while streamlining oversight and reducing maintenance demands.
Beyond basic backup procedures, healthcare organizations should implement immutable storage - a method preventing data modification or deletion for set periods. This approach helps meet strict medical record retention requirements while defending against both malicious and accidental data loss.
The human factor remains a critical vulnerability, with phishing attacks serving as a common entry point for ransomware. A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy must include employee training, role-based access controls, and multi-factor authentication alongside robust backup systems.
As cyberattacks on healthcare continue rising, organizations must adopt layered security approaches to protect patient data and maintain critical care services. The Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) provides extensive guidance for organizations working to strengthen their cybersecurity posture against evolving ransomware threats.