Security researchers have identified a sophisticated new version of the Remcos remote access trojan (RAT) being distributed through phishing attacks. This latest variant employs advanced evasion techniques to avoid detection and infect systems without leaving traces on the hard drive.
The Remcos RAT is a commercially available tool originally designed for legitimate remote administration purposes. However, cybercriminals frequently misuse it to gain unauthorized access to victims' computers and steal sensitive data.
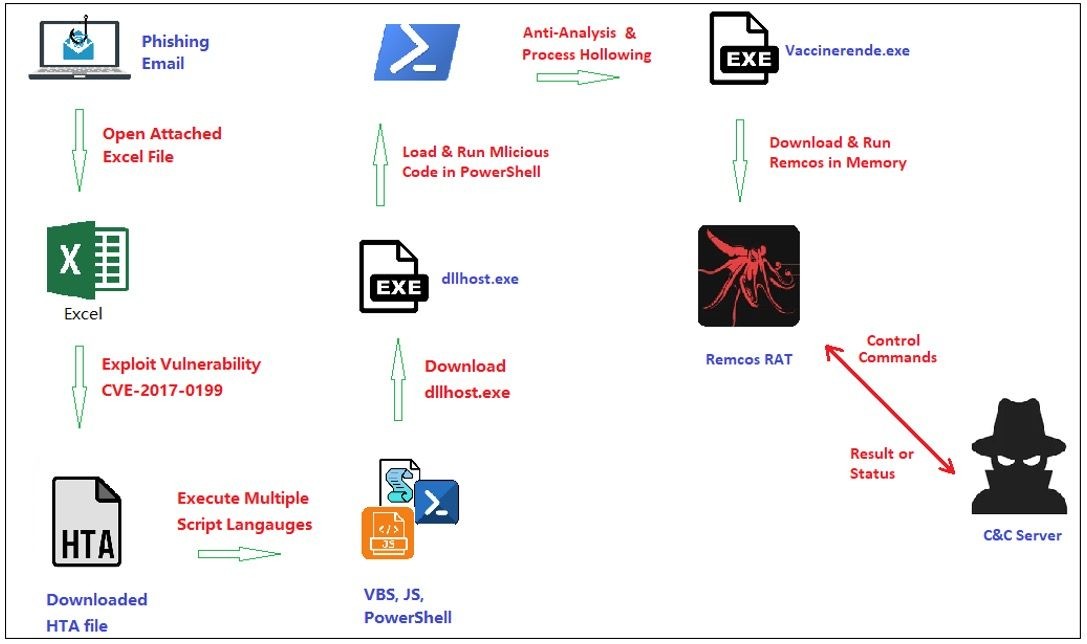
In this newly observed campaign, attackers send phishing emails with a malicious Excel document masquerading as an order file. When unsuspecting recipients open the document, it exploits a known vulnerability to download and execute hidden malicious code on the system.
The attack chain involves multiple stages of obfuscation and evasion:
- The initial Excel file exploits CVE-2017-0199 to download and run an HTA file
- The HTA file contains heavily obfuscated code using various scripting languages
- PowerShell scripts are used to download and execute additional payloads
- Process hollowing techniques inject the final Remcos RAT payload into legitimate processes
By operating entirely in memory and leveraging legitimate Windows processes, this fileless approach makes the malware extremely difficult to detect using traditional antivirus solutions.
Once installed, Remcos provides attackers with extensive remote control capabilities over the infected system. This includes harvesting files, capturing keystrokes and screenshots, activating the webcam and microphone, and executing arbitrary commands.
To maintain long-term access, the malware also adds persistence mechanisms to automatically restart after system reboots.
The discovery of this new Remcos variant highlights the ongoing evolution of malware to evade security controls. Users are advised to exercise caution with unexpected email attachments and keep systems fully patched and updated to protect against such threats.